Tasmania
On this page:
In 2021–22, 24 publicly funded alcohol and other drug treatment agencies in Tasmania provided provided 3,483 treatment episodes to 2,684 clients (tables Agcy.1, SCR.21).
Tasmania reported:
- a 9.7% decrease in treatment episodes from 3,900 in 2020–21 to 3,500 in 2021–22, and a 49% increase in treatment episodes since 2013–14 (2,300) (Table ST TAS.2)
- less clients are using AOD services in 2021–22 than 2013–14, after adjusting for population growth (528 clients per 100,000 population compared with 540 per 100,000, respectively)
- client numbers increased from 2,400 in 2013–14 to 2,700 in 2021–22 (Table SCR.21).
The visualisation shows that 3,483 treatment episodes were provided to 2,684 clients in Tasmania in 2021–22. This equates to a rate of 685 episodes and 528 clients per 100,000 population, lower than the national rate (1,009 episodes and 576 clients per 100,000 population).

In 2021–22, most (86%) clients in Tasmania attended 1 agency, and received an average of 1.3 treatment episodes, which is lower than national average of 1.8 treatment episodes (tables SCR.21, SCR.23).
Client demographics
In 2021–22:
- most (94%) clients in Tasmania received treatment for their own alcohol or drug use, of which 3 in 5 (62%) people were male (Figure TAS 1)
- people seeking treatment for someone else’s alcohol or drug use were most likely to be female (71%)
- half (51%) of all clients were aged 20–39 years
- around 1 in 7 (14%) of all clients identified as Indigenous Australian, which is lower than the national proportion (18%)
- the majority (94%) of all clients were born in Australia and nearly all (99%) reported English as their preferred language (tables SC Tas.1–3, SC.4, SC TAS.21–22).
The grouped horizontal bar chart shows that, in 2021–22, alcohol was the most common principal drug of concern in treatment episodes provided to clients in Tasmania for their own drug use (48.8%). This was followed by amphetamines (21.5%) and cannabis (17.9%). Cannabis was the most common additional drug of concern (16.3% of episodes), followed by amphetamines (9.1%) and alcohol (7.6%).

Patterns of service use
Over the period 2017–18 to 2021–22, 9,900 clients received treatment in Tasmania. Of these clients, the majority received treatment in a single year (74% or 7,300):
- 1,600 (16%) received treatment for the first time in 2021–22
- a further 5,700 (58%) received treatment in only one of the five collection periods (excluding 2021–22) (Table SCR.28).
Drugs of concern
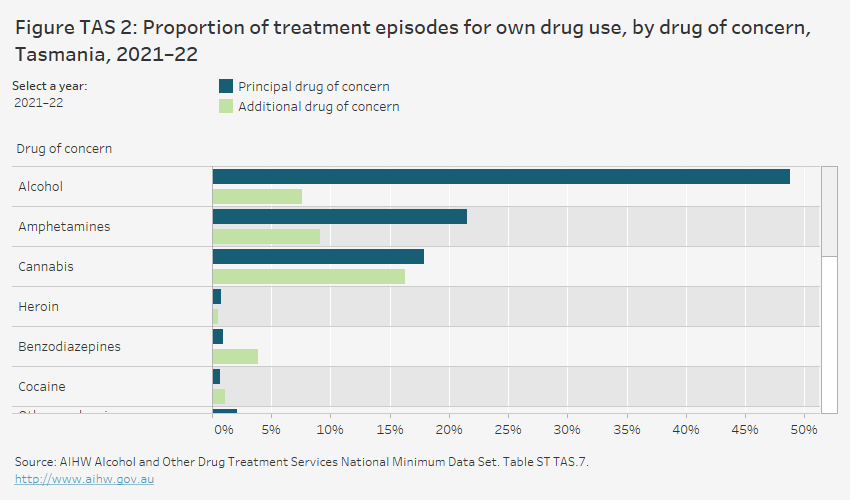
In 2021–22, for clients in Tasmania receiving treatment episodes for their own alcohol or drug use:
- alcohol was the most common principal drug of concern (49% or 1,600 episodes) (Figure TAS 2, Table ST TAS.7)
- amphetamines as a principal drug of concern accounted for 1 in 4 treatment episodes (22% or 710 episodes).
The grouped horizontal bar chart shows that, in 2020–21, alcohol was the most common principal drug of concern in treatment episodes provided to clients in Tasmania for their own drug use (44.8%). This was followed by amphetamines (24.9%) and cannabis (17.5%). Cannabis was the most common additional drug of concern (16.9% of episodes), followed by amphetamines (9.1%) and alcohol (8.3%).
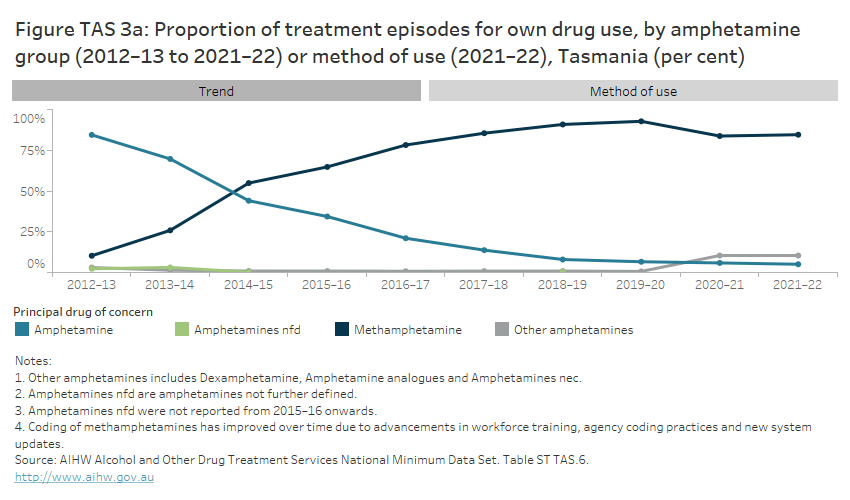
In 2021–22, for clients receiving treatment for their own use of amphetamines:
- methamphetamine was reported as a principal drug of concern in over 8 in 10 (85%) treatment episodes (Figure TAS 3a)
- in almost half (47%) of treatment episodes where methamphetamine was a principal drug of concern, injecting was the most common method of use, followed by smoking (39%) (Figure TAS 3b).
The line graph shows that, from 2012–13 to 2013–14, amphetamine was the most common drug of concern among amphetamine-related treatment episodes for clients’ own drug use. In 2014–15, methamphetamine became the most common drug of concern. The proportion of episodes for methamphetamine increased from 10.3% in 2012–13 to 84.5% in 2021–22, while episodes for amphetamine decreased from 84.4% to 5.1% over the same period. Buttons allow the user to navigate to data for amphetamines by method of use.
Clients can nominate up to 5 additional drugs of concern; these drugs are not necessarily the subject of any treatment within the episode (see technical notes).
In 2021–22, when the client reported additional drugs of concern, cannabis was the most common additional drug of concern (16% of episodes), followed by amphetamines (9%), alcohol and nicotine (both 8%) (Table ST TAS.7).
Over the period 2012–13 to 2021–22:
- alcohol was the most common principal drug of concern, increasing from 39% of episodes in 2012–13 (840 episodes) to 49% (1,600) in 2021–22 (Table ST TAS.7)
- treatment episodes for amphetamines increased from 12% (263 episodes) to 22% (710) over the period
- treatment episodes for cannabis decreased from 30% (638 episodes) to 18% (591). While the number of treatment episodes increased, the proportion in relation to all principal drugs of concern decreased
- within the amphetamines group, methamphetamine was reported as the principal drug of concern in 3% of episodes in 2012–13, rising to 93% in 2019–20, falling to 85% in 2021–22 (Figure TAS 3a). The rise in episodes may be related to increases in funded treatment services and/or improvement in agency coding practices for methamphetamines.
Treatment
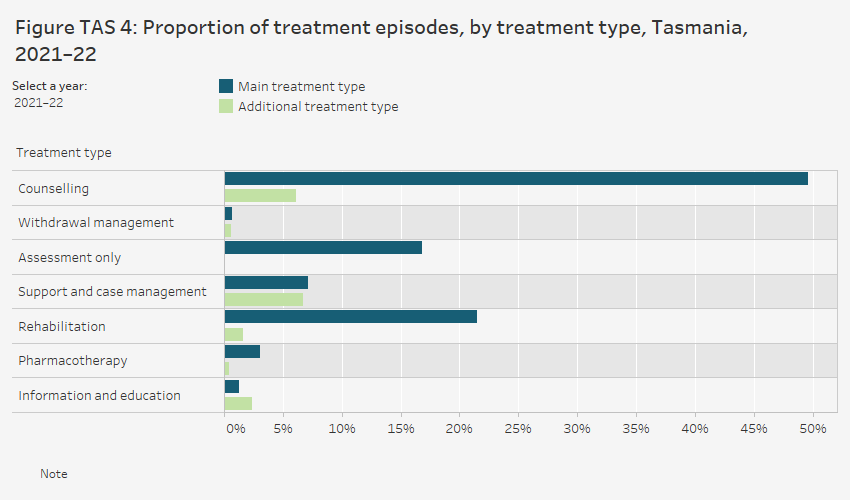
In 2021–22, for treatment episodes in Tasmania:
- counselling was the most common main treatment (50% of episodes), followed by rehabilitation (21%) (Figure TAS 4, Table ST TAS.13)
- where an additional treatment was provided as a supplementary to the main treatment, support and case management (6.7%) was the most common type of additional treatment, followed by counselling (6.1%) and information and education (2.4%). See technical notes for further information on calculating proportions for additional treatment type.
Over the period 2012–13 to 2021–22:
- counselling remained the most common main treatment, with the proportion of episodes peaking at 62% in 2013–14, falling to 37% in 2016–17, before fluctuating between 48% to 50% from 2018–19 onwards
- rehabilitation increased from 2012–13 (6%) peaking in 2016–17 (24%) before decreasing in 2021–22 (21%); the proportion of episodes for rehabilitation is higher than the national proportion over this period (ranging from 4.9–6.5%) (tables ST TAS.13, Trt.1).
The grouped horizontal bar chart shows that, in 2021–22, the most common main treatment type provided to clients in Tasmania for their own drug use was counselling (49.6% of episodes). This was followed by rehabilitation (21.5%) and assessment only (16.8%). Support and case management was the most common additional treatment type (6.7% of episodes), followed by counselling (6.1%).
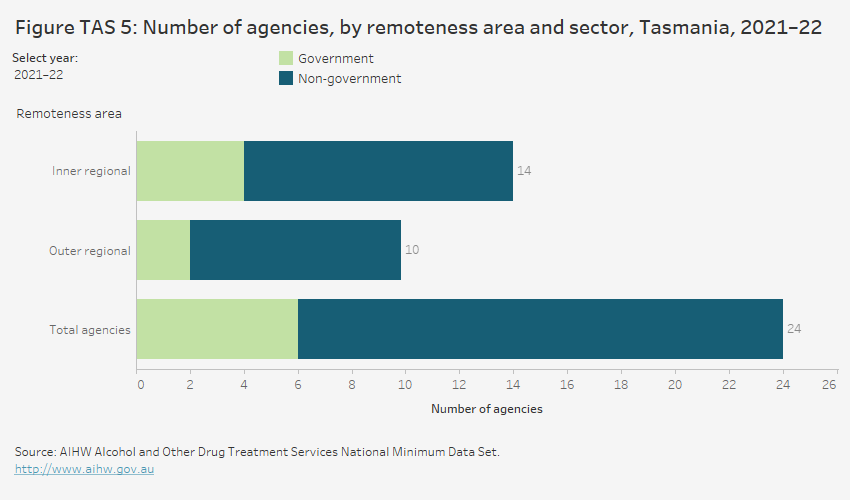
Agencies
Tasmania only has the geographical classifications of Inner regional, Outer regional and Remote areas.
In 2021–22, in Tasmania:
- three-quarters (75%) of the 24 AOD agencies that received public funding were non-government treatment agencies
- 58% of agencies were located in Inner regional areas, followed by Outer regional (42%) (Figure TAS 5, Table Agcy.3)
- agencies located in Inner regional and Outer regional areas were more likely to be non-government organisations.
In the 10 years to 2021–22, the number of publicly funded treatment agencies in Tasmania rose from 17 in 2012–13 to 24 in 2021–22 (Table Agcy.1).
Note that remoteness categories are derived by applying a correspondence based on the agency’s Statistical Area level 2 code (SA2). Not all SA2 codes fit neatly within a single remoteness category, and a ratio is applied to reapportion each SA2 to the applicable remoteness categories. As a result, it is possible that the number of agencies in a particular remoteness category is not a whole number. After rounding, this can result in there being ‘<0.5%’ agencies in a remoteness area, due to the agency’s SA2 partially crossing into the remoteness area. See technical notes for further details.
The horizontal bar chart shows that most treatment agencies in Tasmania were located in Inner regional areas (14 agencies), followed by Outer regional areas (10 agencies) in 2021–22. Of the total 24 treatment agencies, most (18 agencies) were non-government agencies.