Physical inactivity
In 2018, physical inactivity accounted for 2.5% of the total disease burden in Australia.
These estimates reflect the amount of disease burden that could have been avoided if all people in Australia were sufficiently physically active (see ABDS 2018 Risk factor estimates data table).
Physical inactivity was causally linked to the burden from type 2 diabetes, bowel cancer, dementia, coronary heart disease and stroke, as well as uterine and breast cancer in females.
How much burden was attributable to physical inactivity?
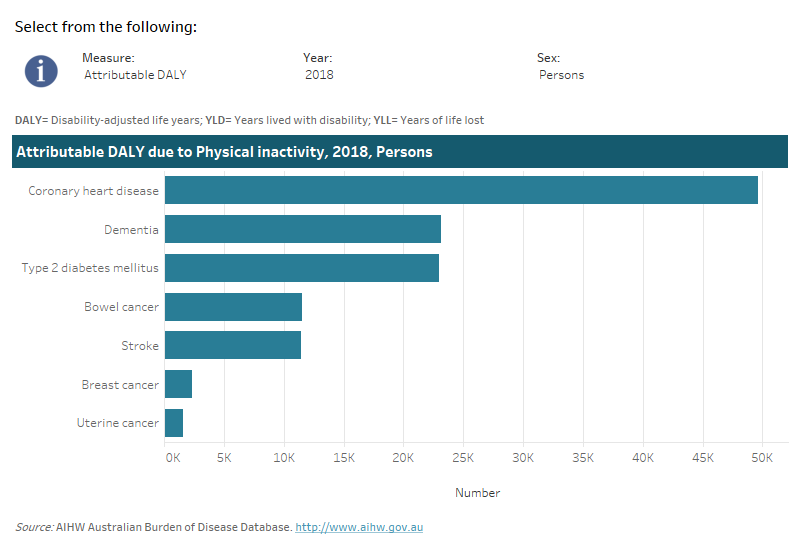
In 2018, physical inactivity was responsible for 20% of the total disease burden due to type 2 diabetes, 17% of the uterine cancer burden, 16% of coronary heart disease burden, 12% of dementia burden, 12% due to bowel cancer, 9% of stroke burden and 3% of breast cancer.
This interactive data visualisation shows the burden attributable to physical inactivity by linked disease. The main section shows a horizontal bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden of the disease linked to physical inactivity.
How did burden attributable to physical inactivity vary by age and sex?
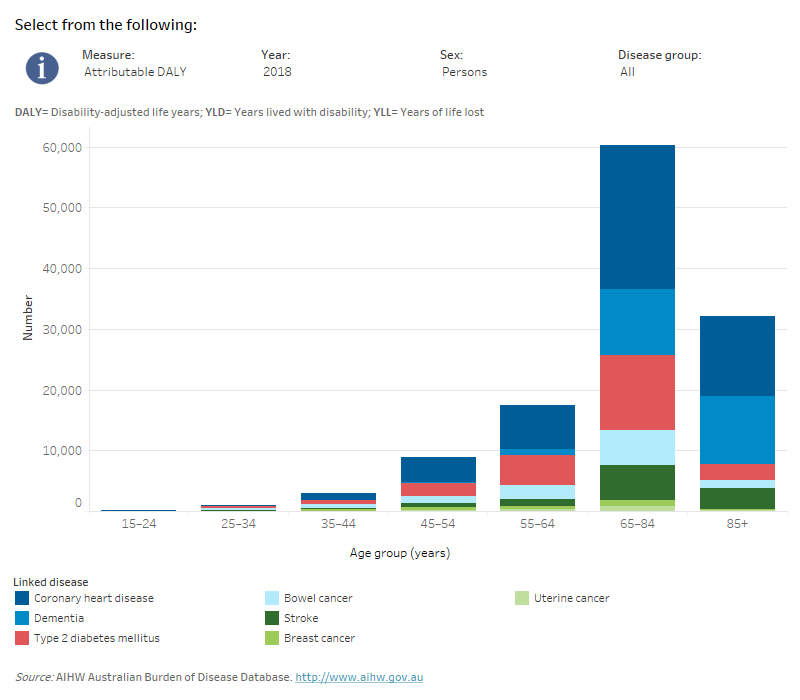
Disease burden due to physical inactivity was measured in people aged 15 and over. Total burden due to physical inactivity was low in people aged 15–34 and increased with age, peaking in ages 65–84.
In males of all ages, the most burden due to physical inactivity was from coronary heart disease.
By comparison, in females aged 55–64 years, the most burden due to physical inactivity was from type 2 diabetes. Among females aged 65–84 years, the most burden due to physical inactivity was from coronary heart disease. For females aged 85 and over, the most burden was from dementia.
This interactive data visualisation shows the amount of burden attributable to physical inactivity by age group and linked disease. The main section shows a stacked bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex, disease group and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden within a particular age group. Each bar is also split into separate components with each colour representing a disease linked to physical inactivity.
This interactive data visualisation shows the rate of burden attributable to physical inactivity by socioeconomic group. The main section shows a bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden within a particular socioeconomic group due to physical inactivity.

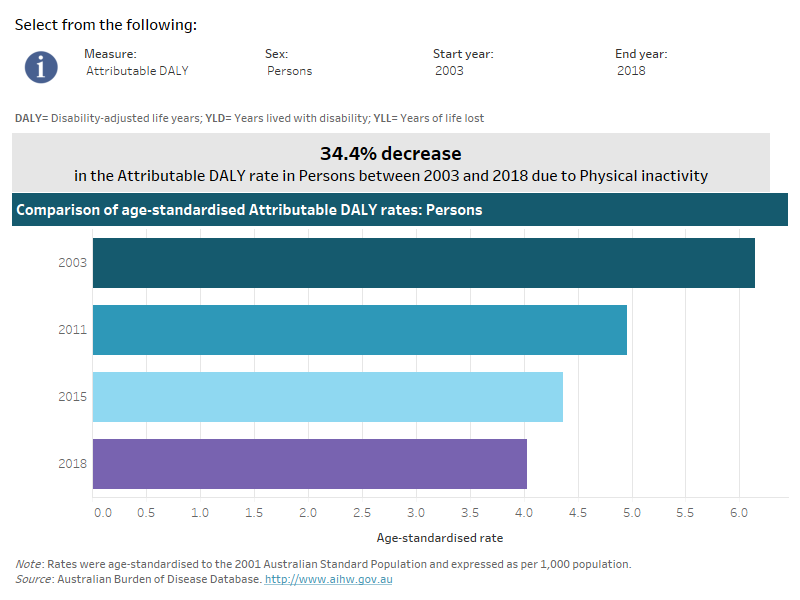
This interactive data visualisation shows the rate of burden attributable to physical inactivity by year. The main section shows a horizontal bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden within a particular year due to physical inactivity.