Maternity carers
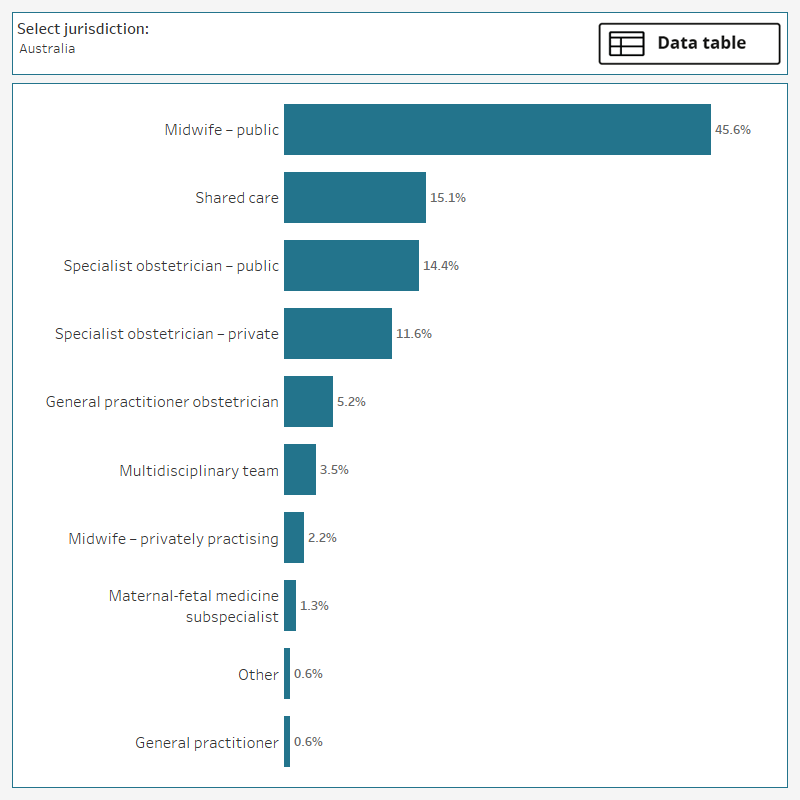
The designated or lead maternity carer is the health professional coordinating the care for women during the antenatal, intrapartum, and postnatal periods. Just under half of all models of care (46%) have a midwife – public (midwives employed in the public health system) as the designated carer. This is an essential component of all models classified as midwifery group practice caseload care (100%) and is also found in nearly two-thirds of models classified as public hospital maternity care (64%). The next most common designated carer is a shared care arrangement (15% of models), followed by a specialist obstetrician – public (14%), and a specialist obstetrician – private (12%). Having a shared care arrangement means the model of care does not have a single designated carer and the carer may change at different times or be shared.
Collaborative maternity carers are other health professionals that work in partnership with the designated carer to provide maternity care. Most (96%) models of care have at least one collaborative carer, in addition to the lead or designated carer. Half (52%) of all models of care have one collaborative carer, and this is higher in models classified as private obstetrician specialist care (85%), GP obstetrician care (85%), and remote area maternity care (69%). Just over one-quarter of models (28%) have 2 collaborative carers, and this is higher in models classified as combined care (50%) and shared care (42%).
Common collaborative carers include a specialist obstetrician – public (46% of models), a midwife – public (44%) and a GP obstetrician (16%). All models of care with a designated carer of specialist obstetrician – public have a midwife – public as a collaborative carer, while just under three-quarters (71%) of models with a midwife – public as a designated carer have a specialist obstetrician – public as a collaborative carer. In models with a designated carer of shared care, most (92%) have a midwife – public as a collaborative carer, half (50%) have a specialist obstetrician – public; as a collaborative carer and 44% have a GP obstetrician as a collaborative carer.
A midwife – public is the designated carer in 46% of models nationally and the most common designated carer across all jurisdictions; it is more common in models of care in Tasmania (65%) and New South Wales (57%). Victoria and the Australian Capital Territory have a higher proportion of models of care with a specialist obstetrician – private as the designated carer (19% and 18% respectively, compared with 12% overall).
The data visualisation below (Figure 3) shows maternity models of care by type of designated carer. Select from the drop-down menu to filter by jurisdiction (state or territory). Use the button to access the data table.
Figure 3: Proportion of models of care, by type of designated carer, Australia, 2023
The bar chart shows around 46% of models of care have a midwife – public as the designated or lead carer. The next is a shared care arrangement at 15.1%
Notes
- A designated carer (otherwise known as the lead carer) is the health professional coordinating the care for women during the antenatal, intrapartum and postnatal periods.
- Analyses are based on the models of care being used by maternity services with birthing facilities that were classified in the MoC NBPDS in June 2023.
Source: AIHW analysis of the MoC NBPDS.


