Measuring overweight and obesity
On this page:
Body Mass Index
Body Mass Index (BMI) is an internationally recognised standard for classifying overweight and obesity in adults. BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in metres.
BMI does not necessarily reflect body fat distribution or describe the same degree of fatness in different individuals. However, at a population level, BMI is a practical and useful measure for identifying overweight and obesity. Figure 1 can be used to calculate your BMI.
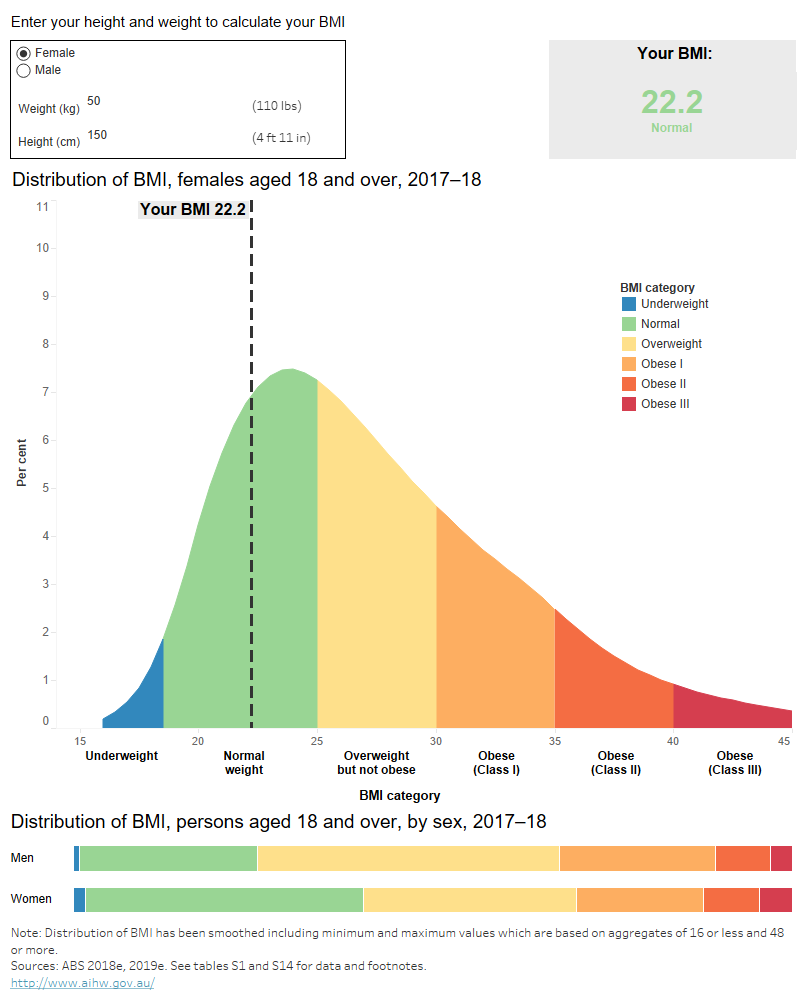
Figure 1: BMI calculator and distribution, persons aged 18 and over, by sex, 2017–18
Figure 1: BMI calculator and distribution, persons aged 18 and over, by sex, 2017–18.
This body mass index (BMI) calculator allows you to calculate your BMI by entering your sex, height and weight. These graphs show the distribution of BMI values by sex and the proportion of men and women in each BMI category in 2017–18. The most common category is normal weight (39%) for women and overweight but not obese (42%) for men.
| BMI (kg/m²) | Classification |
|---|---|
| Less than 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 to less than 25 | Normal weight |
| 25 or more | Overweight or obese |
| 25 to less than 30 | Overweight but not obese |
| 30 or more | Obese |
| 30 to less than 35 | Obese class I |
| 35 to less than 40 | Obese class II |
| 40 or more | Obese class III |
Source: (WHO 2000).
Height and body composition are continually changing for children and adolescents as they grow. Different BMI cut-off points based on age and sex are used when assessing their BMI at a population level (Cole, et al. 2000).
Waist circumference
Waist circumference is an alternative way to assess the risk of developing obesity-related chronic diseases. A higher waist measurement is associated with an increased risk of chronic disease. The threshold at which waist circumference indicates an increased risk of developing disease are dependent on gender and ethnicity (NHMRC 2013). The threshold may also be less accurate in some situations such as pregnancy and medical conditions where there is distension of the abdomen (Heart and Foundation 2023). The risk levels presented below are for Caucasian men and women.
| Sex | Increased risk | Substantially increased risk |
|---|---|---|
| men | 94cm | 102cm |
| women | 80cm | 88cm |
For information on how to correctly measure your waist, visit the National Heart Foundation website,
Cole T, Bellizzi M, Flegal K and Dietz W (2000) 'Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey', BMJ, 320(1240-1243, https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.320.7244.1240.
Heart Foundation (2023) What is a healthy body weight?, heartfoundation.org.au, accessed 29 March 2023.
NHMRC (National Health and Medical Research Council) (2013) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of overweight and obesity, nhmrc.gov.au, accessed 29 March 2023.
WHO (World Health Organization) (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic; Report of a WHO consultation, World Health Organization Technical Report Series 894, who.int, accessed 9 November 2020.


