Impaired kidney function
In 2018, 5.0% of the total disease burden among Indigenous Australians was due to impaired kidney function (including chronic kidney disease), making it the 8th leading risk factor contributing to total disease burden.
These estimates reflect the amount of burden that could have been avoided if all Indigenous Australians did not have impaired kidney function.
Impaired kidney function was causally linked to 6 diseases—chronic kidney disease, coronary heart disease, dementia, stroke, gout and peripheral vascular disease (see ABDS 2018 Risk factor estimates for Indigenous Australians data table S1).
How much burden was attributable to impaired kidney function?
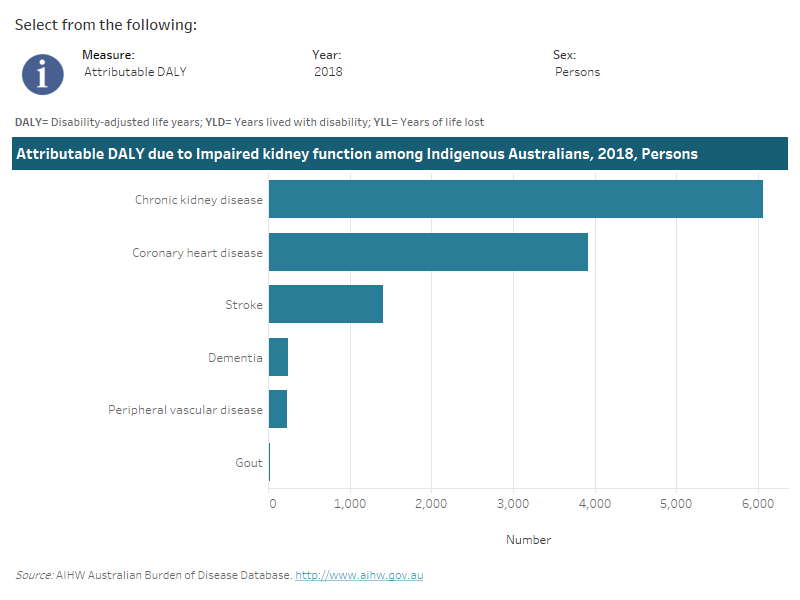
In 2018 among Indigenous Australians, impaired kidney function was responsible for the entire burden of chronic kidney disease, 69% of peripheral vascular disease burden, 45% of stroke burden, 28% of coronary heart disease, 19% of gout burden, and 7% of dementia burden.
This interactive data visualisation shows the burden attributable to impaired kidney function among Indigenous Australians by linked disease. The main section shows a horizontal bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden of the disease linked to impaired kidney function.
How did burden attributable to impaired kidney function vary by age and sex?
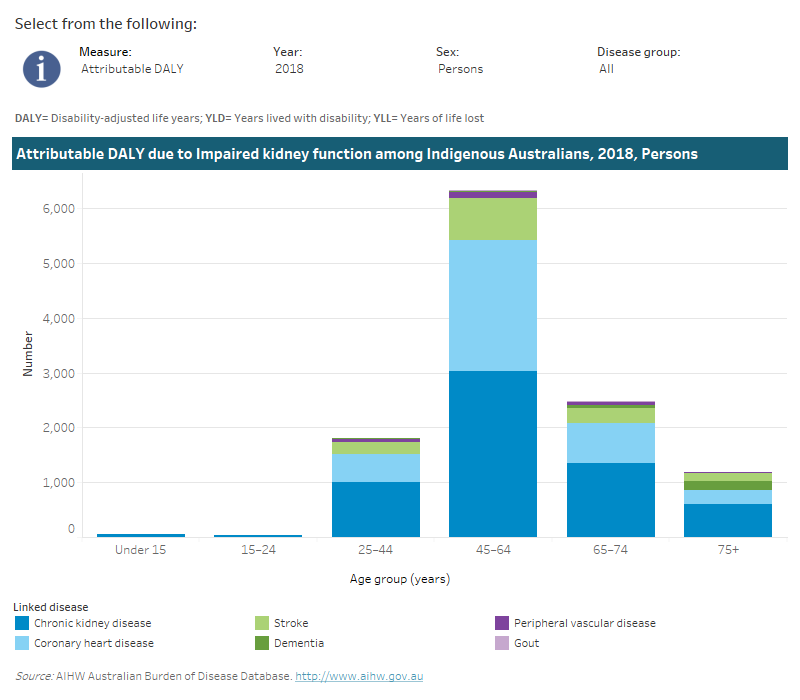
The majority of the total burden due to impaired kidney function among Indigenous Australians occurred among those aged between 45 and 74. Across all age groups the most burden due to impaired kidney function was from chronic kidney disease and coronary heart disease. This was similar for both Indigenous males and Indigenous females.
This interactive data visualisation shows the amount of burden attributable to impaired kidney function among Indigenous Australians by age group and linked disease. The main section shows a stacked bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex, disease group and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden within a particular age group. Each bar is also split into separate components with each colour representing a disease linked to impaired kidney function.
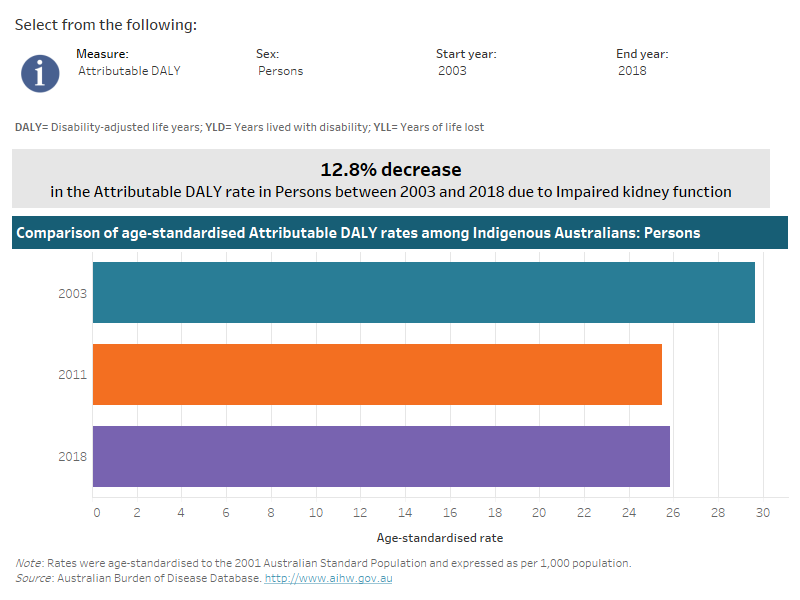
This interactive data visualisation shows the rate of burden attributable to impaired kidney function among Indigenous Australians by year. The main section shows a horizontal bar graph which can be customised to report data according to year, sex and measure of attributable burden. Each bar represents the attributable burden within a particular year due to impaired kidney function.